Description
In an era where artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the contours of creativity and productivity, the realm of Generative AI (AIGC) emerges as a beacon of innovation. This article investigates the comprehensive survey provided by “A Complete Survey on Generative AI (AIGC): Is ChatGPT from GPT-4 to GPT-5 All You Need?” to unravel the complexities, potentials, and transformative power of generative AI across various industries and applications.
The Foundation of Generative AI
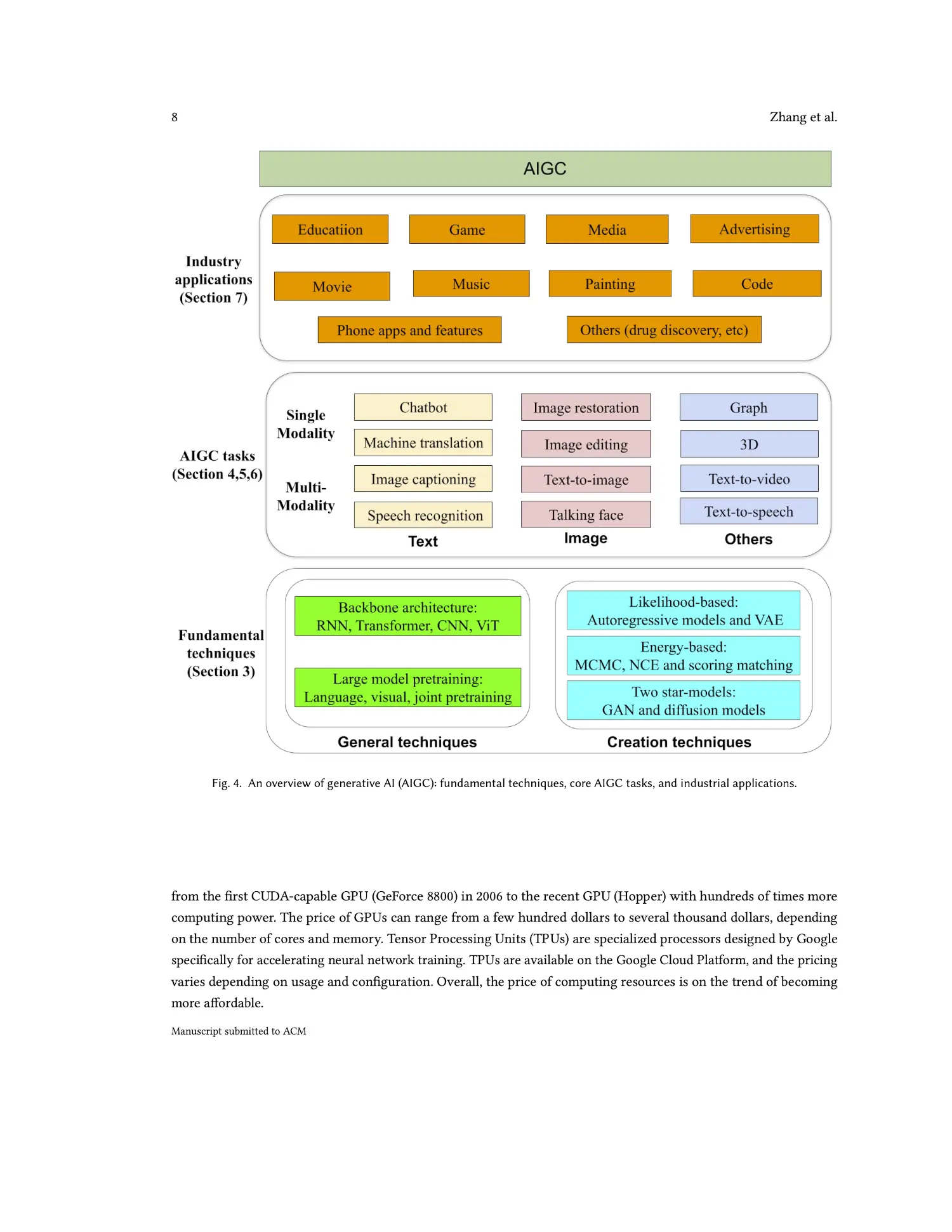
Generative AI, distinct from conventional AI’s focus on analysis and classification, propels the digital frontier forward by creating new, original content. This capability springs from an intricate blend of generative and creation techniques, including the revolutionary Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and the backbone architectures like Transformers. These technical foundations enable AIGC to perform a wide array of tasks, from text and image generation to complex 3D modeling and speech synthesis.
Diverse Applications Across Industries
The survey highlights AIGC’s expansive role across multiple sectors. In education, generative AI tailors learning experiences, offering personalized content and interactive tutoring systems. The gaming and metaverse domains leverage AIGC for creating dynamic, user-driven narratives and environments, while in media and advertising, it streamlines content creation and offers novel ways to engage audiences. The generative AI’s transformative capabilities are being harnessed across various sectors, beyond the initial examples of education, gaming, metaverse, media, and advertising. Let’s explore additional industries where AIGC is making a significant impact, showcasing its versatility and potential for innovation.
Healthcare and Biotech
In the healthcare and biotech industries, generative AI is revolutionizing the way treatments are developed and personalized. By analyzing vast datasets of patient information, AIGC can identify patterns and predict outcomes that would be impossible for humans to discern, leading to breakthroughs in personalized medicine. For instance, generative models are being used to design new drugs by simulating how different molecular structures could interact with biological targets. Additionally, AI generated models of diseases allow for the rapid testing of potential treatments in a virtual environment, significantly accelerating the research and development process.
Architecture and Urban Planning
Architecture and urban planning are also benefiting from the capabilities of generative AI. By inputting design parameters and constraints, architects and planners can use AIGC to generate a range of innovative design solutions that optimize for aesthetics, functionality, and sustainability. These AI-driven tools can simulate how buildings will perform in various environmental conditions, aiding in the creation of more resilient and energy-efficient structures. Moreover, generative models are being employed to envision urban layouts that optimize traffic flow, reduce congestion, and enhance livability, showcasing the potential of AI in creating smarter cities.
Fashion and Design
The fashion and design sectors are harnessing generative AI to push the boundaries of creativity and customization. AIGC can generate unique patterns, textures, and designs based on emerging trends, personal preferences, or even historical fashion data, offering brands a tool for creating highly personalized and innovative products. Additionally, AI-driven tools enable designers to experiment with virtual prototypes before production, reducing waste and enhancing the sustainability of design processes.
Legal and Financial Services
In legal and financial services, generative AI is being explored for its potential to automate and optimize various tasks. For example, AI can generate legal documents or contracts based on specific requirements, saving time and reducing human error. In finance, generative models predict market trends and generate investment strategies by analyzing vast quantities of data, offering insights that can enhance decision-making and risk management.
Agriculture and Environmental Management
Finally, in agriculture and environmental management, generative AI plays a critical role in optimizing resource use and improving yield predictions. By analyzing data from satellite images, weather patterns, and soil conditions, AIGC can generate planting strategies that maximize crop yields while minimizing environmental impact. Furthermore, generative models are being used to simulate environmental changes and assess the potential effects of different conservation strategies, aiding in the fight against climate change and biodiversity loss.
The Evolution of Content Creation
Generative AI, which diverges fundamentally from the traditional AI focus on analysis and classification, is at the forefront of pushing the boundaries of the digital era. Unlike conventional AI, which interprets and acts upon existing data, generative AI embarks on the ambitious journey of creating entirely new, original content. This innovative capability is underpinned by a sophisticated blend of techniques that not only include but also go beyond Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and transformative architectures like Transformers.
Generative Techniques and Architectures
Generative AI leverages generative techniques such as GANs, a groundbreaking framework where two neural networks—generative and discriminative—work in tandem. The generative network generates new data instances, while the discriminative network evaluates them. This dynamic interaction facilitates the production of highly realistic outputs, from synthesizing photographs that seem as if they were taken from the real world to creating art that rivals human-made pieces. An exemplar of GANs’ prowess is seen in the realm of art generation, where models like DALL-E and Artbreeder have revolutionized how we perceive and create art, enabling the synthesis of images that blend various artistic styles or even generate entirely novel aesthetics.
Transformers, another pillar of generative AI, have significantly impacted the field, particularly in natural language processing (NLP) and beyond. Originally designed for tasks such as translation and text summarization, Transformers’ ability to handle sequential data has been a game-changer. Their architecture, which allows for parallel processing of data and attention mechanisms focusing on different parts of the input data, has proven exceptionally effective in understanding context and generating coherent and contextually relevant text. ChatGPT, a variant of the GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) models, exemplifies the capability of Transformers to generate human-like text, engage in meaningful conversations, write poetry, or even generate code.
From Text and Image Generation to Complex 3D Modeling and Speech Synthesis
The versatility of generative AI extends far beyond text and image creation, embracing complex tasks such as 3D modeling and speech synthesis. In 3D modeling, generative AI has introduced methods to create detailed and intricate models from simple textual descriptions or 2D images, revolutionizing industries such as gaming, film, and virtual reality. This capability allows for the rapid prototyping of environments and characters, significantly reducing the time and effort required in traditional 3D modeling workflows.
Speech synthesis, another frontier of generative AI, has seen remarkable advancements with models capable of generating human-like speech from text. These models can capture the nuances of human speech, including tone, emotion, and style, making them invaluable in applications ranging from virtual assistants to accessible technologies for the visually impaired. Tools like Google’s WaveNet and Tacotron have showcased the potential of generative AI in creating natural, dynamic speech, blurring the lines between synthesized and real human voices.
The foundational techniques of generative AI, from GANs to Transformers, have enabled a leap forward in the creation of digital content. By enabling the generation of new, original content across text, images, complex 3D models, and speech, generative AI has not only expanded the realm of possibility for creative expression but also set new benchmarks in the realism and applicability of AI-generated outputs. These advancements underscore the transformative impact of generative AI, marking it as a cornerstone of the next generation of digital innovation.
Ethical Considerations and Future Outlook
As generative AI continues to evolve, it brings forth ethical considerations and challenges, including concerns over copyright, privacy, and the amplification of biases. The survey calls for a balanced approach, advocating for the responsible use of AI technologies while exploring their immense potentials.
Looking ahead, the survey suggests an exciting trajectory for generative AI, with ongoing advancements likely to offer even greater control and flexibility in content creation. The shift from pretraining to fine-tuning models suggests a future where AI can be more effectively tailored to specific tasks and applications, from enhancing creativity in the arts to driving innovation in industries like healthcare and engineering.
Investment, Bubble, and Job Opportunities
The discussion extends to the economic and employment implications of generative AI. While there is enthusiasm around the investment and potential of AIGC, debates about its long-term sustainability and impact on the job market persist. However, the survey underscores the potential for generative AI to create new job opportunities, particularly in AI research and development, even as it transforms existing roles.
Let’s look into the investment landscape, concerns about a potential bubble, and the evolving job market influenced by AIGC technologies.
Investment Landscape in Generative AI
The investment in generative AI has been surging, driven by its potential to revolutionize a wide array of industries. Venture capitalists and tech giants alike are pouring resources into AIGC startups and projects, betting on their ability to deliver innovative solutions and disrupt traditional markets. This influx of capital has accelerated the development of AIGC technologies, fostering a competitive environment that pushes the boundaries of what AI can achieve. However, this rapid investment growth raises questions about valuation and the risk of an investment bubble. Comparisons are often made to previous tech bubbles, with skeptics pointing to inflated expectations and the uncertain path to profitability for many AIGC ventures.
The Bubble Debate
The debate around a potential generative AI bubble centers on the disparity between the high valuations of AI startups and the tangible value they currently deliver. Critics argue that while the technology holds promise, the monetization strategies and business models of many AIGC companies remain unproven at scale. The concern is that without clear, sustainable revenue streams, the sector could face a correction. Proponents counter that the transformative potential of AIGC justifies the investment, pointing to the long-term impact these technologies are likely to have across sectors, from healthcare to entertainment, suggesting that the current enthusiasm is not merely speculative but grounded in a vision of profound technological shift.
Job Opportunities and Workforce Transformation
The impact of generative AI on the job market is multifaceted, presenting both challenges and opportunities. On one hand, AIGC is expected to automate tasks that were previously thought to require human creativity, raising concerns about job displacement in fields like content creation, design, and even certain aspects of software development. On the other hand, the survey highlights the emergence of new job opportunities within AI research, development, and application. The demand for AI specialists, data scientists, ethicists, and regulatory experts is expected to grow as businesses and societies navigate the integration of AIGC technologies. Furthermore, generative AI is likely to spawn entirely new industries and services, creating roles that do not yet exist but will become essential as the technology matures and proliferates.
Navigating the Transition
The transition to an economy increasingly influenced by generative AI necessitates thoughtful policy and educational responses. Upskilling and reskilling initiatives will be crucial in preparing the workforce for new types of employment opportunities. Additionally, there is a need for a dialogue between technologists, policymakers, and educators to ensure that the benefits of AIGC are broadly distributed and that societies can adapt to the changing nature of work. This includes addressing the ethical and social implications of automated content creation and ensuring that AIGC technologies are developed and used in ways that enhance human capabilities rather than replace them.
Conclusion: Navigating the Generative AI Landscape
In sum, “A Complete Survey on Generative AI (AIGC)” offers a rich, nuanced exploration of the state and future of generative AI. From GPT-4 to GPT-5 and beyond, the journey of AIGC is marked by rapid advancements, expanding applications, and profound implications for society. As we stand on the brink of this AI-driven revolution, the survey serves as both a roadmap and a reflection on how we might navigate the exciting yet uncharted waters of generative AI.
Reference
Zhang, C., Zhang, C., Zheng, S., Qiao, Y., Li, C., Zhang, M., Dam, S. K., Thwal, C. M., Tun, Y. L., Huy, L. L., kim, D., Bae, S.-H., Lee, L.-H., Yang, Y., Shen, H. T., Kweon, I. S., & Hong, C. S. (2023). A Complete Survey on Generative AI (AIGC): Is ChatGPT from GPT-4 to GPT-5 All You Need? (arXiv:2303.11717). arXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.11717
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.